Non-Surgical
Minimally Invasive
Natural
SUBSCRIBE TO OUR REGENERATIVE MEDICINE INFORMATION GUIDE
Signup to receive our Patient Guide to Regenerative Medicine
Our Patient Guide to Regenerative Medicine explains more about how we are different. Check your junk mail if you don't receive the e-mail shortly.
With each passing day, your body becomes less efficient at recovery and repair.
YOU can choose a different path.
Regenerative Cellular Therapies rely on advanced technologies to harness and enhance the body’s natural ability to heal, repair, and recover function.
Injuries, surgery, medical treatments, or the normal process of aging can lead to damage and degeneration. Regenerative Cellular Therapies deliver injections of regenerative cellular tissues, growth factors, or other natural healing substances to help the body rebuild and recover function—naturally and without drugs or surgery. It can help with any of the following:
What Our Patients are Saying
Joanne D.
Dr. Kelley is a top-notch professional, who brings resolute care and concern to her patient’s comfort and well-being. You will be very pleased with the treatment provided there. The office is very friendly while maintaining professional and efficient standards of service. You won’t be disappointed!
Regenerative Cellular Therapies We Offer
Our team of medical and healthcare professionals at Thrive! Wellness Center is dedicated to bringing you the safest and most effective Regenerative Cellular Therapies available. We offer Regenerative Cellular Therapies sourced from an FDA-regulated multi-state tissue bank. Therapies may include amniotic fluid, umbilical cord tissue, or other cellular products. Here are some of the therapies we use most often with our patients:
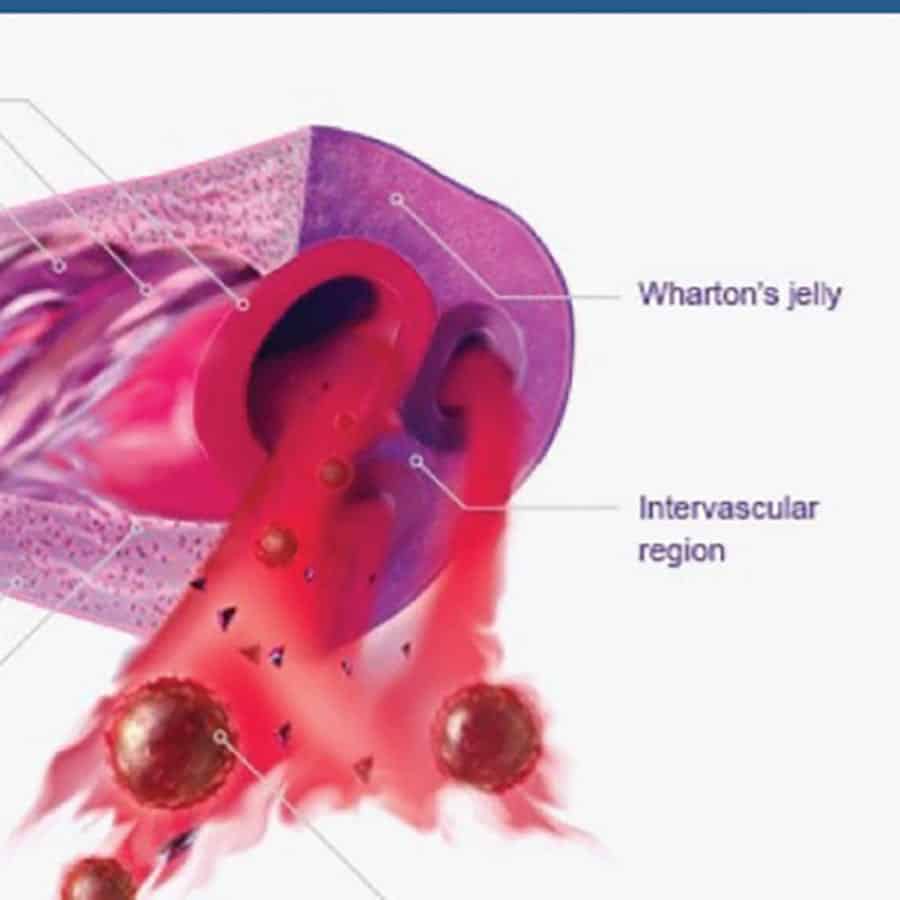
MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS (MSCS) FROM WHARTON’S JELLY
Wharton’s Jelly is derived from umbilical cord tissue. It’s collected after childbirth from healthy donors and does not harm the mother or baby. Wharton’s Jelly is a rich source of Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs), growth factors, and other proteins. It is an “immune privileged” tissue, which means it will not trigger an immune response or rejection. This healing infusion can reduce pain, decrease inflammation, repair cartilage, and restore healthy function in damaged tissues. Learn more.
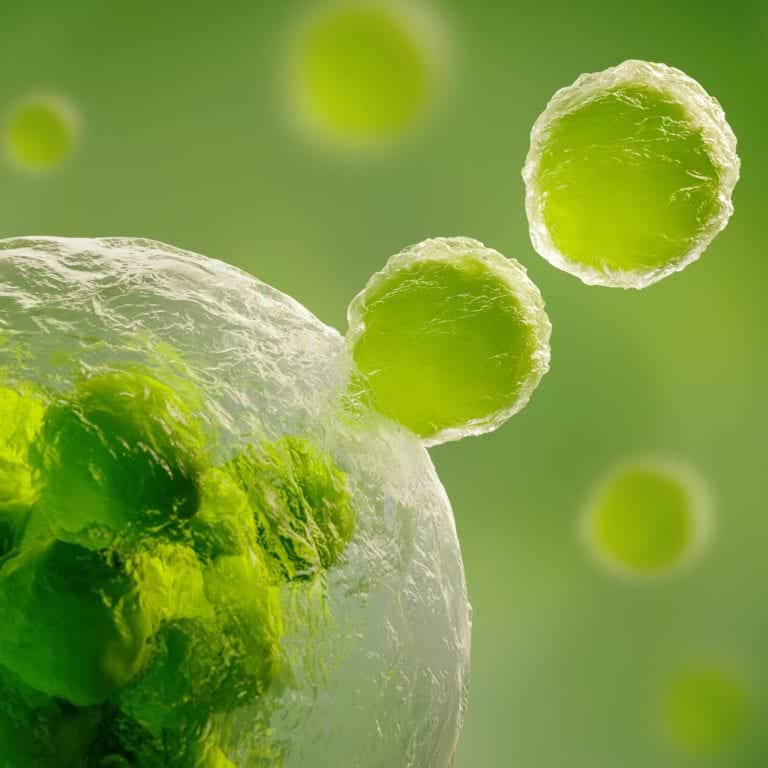
EXOSOMES
Exosomes are fluid-filled packets that are found in all body tissues. They are a rich source of amino acids, collagen, and elastin. They contain substantially more growth factors than adult stem cells and are vital to the process of regeneration and repair. One of the most exciting things about exosomes is that they’re able to cross the blood-brain barrier to support brain health. Exosomes contain no DNA and do not pose a risk of triggering an immune response or rejection. Exosomes can help to alleviate pain and renew function. Learn more.
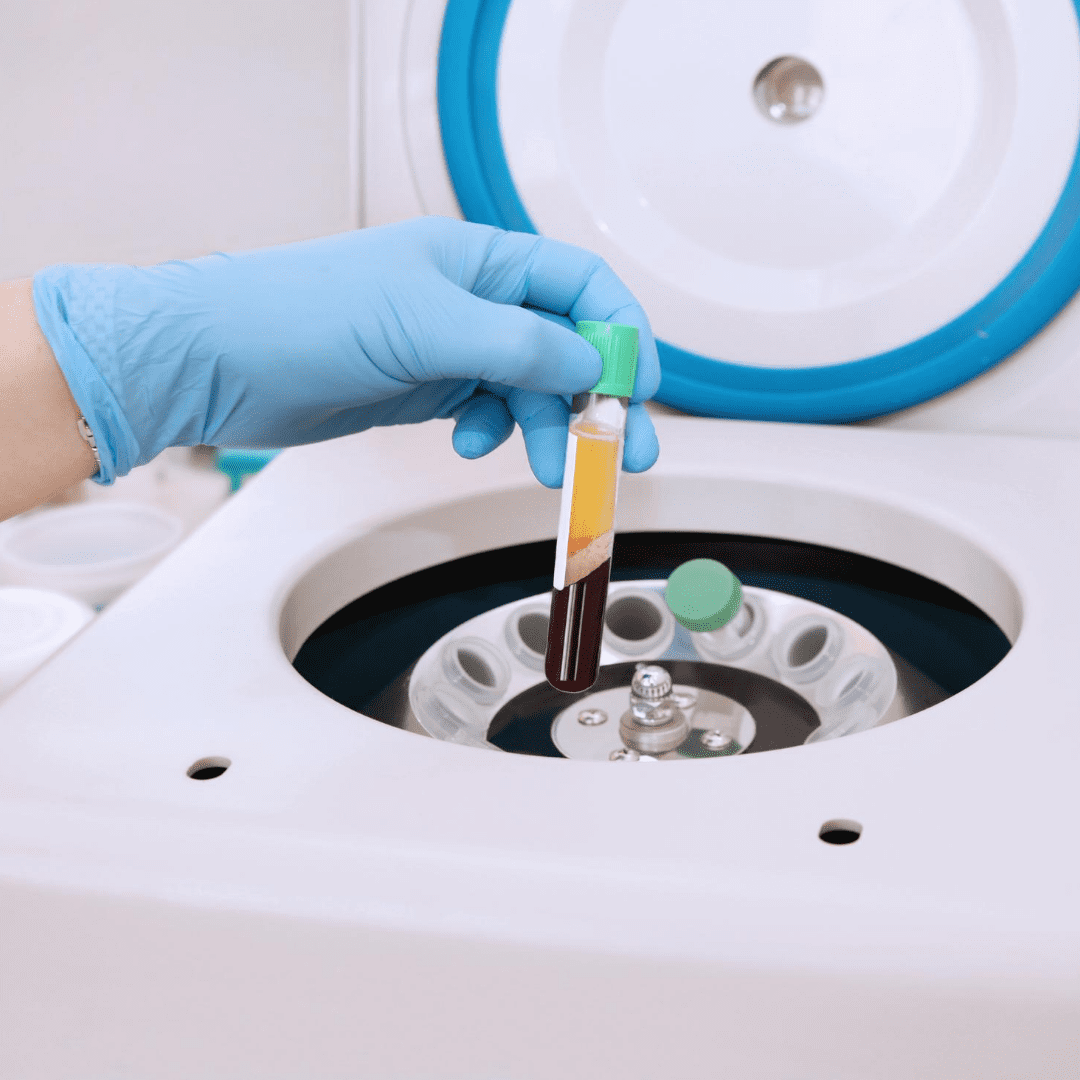

PLATELET-RICH PLASMA (PRP)
PRP is a concentrated preparation of the most healing components from your own blood. The process involves a simple blood draw, preparation of the PRP, and then injection into the damaged or injured area. PRP contains platelets, cytokines, white blood cells, growth factors, and signaling molecules to coordinate the repair process. It can be used alone or in combination with other Regenerative Cellular Therapies. Learn More.
HYALURONIC ACID (HA)
Hyaluronic Acid is a naturally occurring molecule that helps to retain water in the skin. We produce less Hyaluronic Acid as we age, causing the skin to become thin, lined, or droopy. Local injections of Hyaluronic Acid help keep the skin plump and firm as part of our facial rejuvenation program.

NUTRITIONAL IVS
Nutritional IVs give your body a powerful boost of vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients to reduce inflammation, boost antioxidant defenses, support immunity, and more. We may recommend Nutritional IVs along with other Regenerative Cellular Therapies to promote healing from the inside out. Options include high-dose vitamin C, Myer’s cocktail, glutathione, zinc, and other nutrients for energy and rejuvenation. Learn more.
What To Expect
Preliminary Consultation
We offer a complimentary 60-minute consultation to review your health history and discuss your goals. We may also request previous records at this time. You can book this consultation in our convenient online scheduler.
Recommendation and Plan
Based on a review of your health history, our medical team will recommend a plan for Regenerative Cellular Therapies to meet your goals. We will explain this plan at your second visit. If you decide to proceed, you may receive your first treatment session the same day.
Personalized Therapy
Your Regenerative Cellular Therapy treatments will be customized to you. They may include a personalized combination of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Wharton’s Jelly, Exosomes, PRP, HA, or Nutritional IVs to help you repair degenerative changes, recover optimal function, and enjoy youthful vitality.
Health is a Choice!
You can choose to grow old with vitality or get old with disease. Regenerative Cellular Therapies help you recover optimal function for a more youthful and revitalized life.
Regenerative medicine is the process of replacing human or animal cells, tissues, and organs with
new ones. It has the potential to improve health in people who are in poor health. Various techniques
are available, including cell therapy and platelet-rich plasma therapy. These techniques can also be
used to grow artificial organs.
Mesenchymal stem cells
Mesenchymal stem cells are a promising new option for cell treatment and tissue regeneration. They
possess a multipotent state and the ability to differentiate into specific types of cells and tissues.
These cells have many beneficial properties, such as anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory
functions, and have the potential to treat many different conditions. In addition to these properties,
they are also able to home to injury sites and secrete bioactive molecules.
For example, human corneal stem cells transplanted into mice have grown into a fully functional
human cornea. The ability to regenerate human corneal tissue is important in the treatment of
corneal disorders. Muscle tissue regeneration can also be achieved through tissue engineering
technology. Encapsulating mouse or human derived MABs can express a placental-derived growth
factor, which can be used to generate artificial muscles.
In addition to promoting tissue regeneration, MSCs are capable of secreting cytokines and diverse
cell lineages. This differentiation potential is making MSCs an increasingly important source of
therapeutics in regenerative medicine. For example, MSCs can differentiate into islet cells, which
secrete insulin and glucagon, or into different types of skin cells. They have also been found to
improve wound healing, and promote tissue repair via the secretion of cytokines.
Another application of MSCs in regenerative medicine is osteoarthritis, which affects the cartilage on
the ends of bones. By injecting MSCs into affected joints, doctors can reduce pain and improve joint
movement, and increase cartilage thickness. In addition to osteoarthritis, MSC injections have also
proven successful for ligament injuries. These injuries are often very difficult to heal. The process
often leads to extensive swelling, and the reconstructed tissue is often weaker than the original
tissue.
The therapeutic potential of Mesenchymal stem cells is now being studied in numerous fields,
including cancer, autoimmune diseases, and muscle damage. Although the technology is still in its
early stages, it is expected to prove highly beneficial for a variety of diseases.
Platelet-rich plasma therapy
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is a type of treatment involving injections of components of a patient's
own blood into damaged areas. It has been proven effective in a variety of conditions including
degenerated or torn meniscus, shoulder labral tears, and soft tissue injuries. The scientific literature
is full of reports of patients who have benefited from PRP therapy.
Platelet-rich plasma therapy is a drug-free procedure that stimulates the body's natural healing
processes to promote tissue repair and regeneration. It is a fast, painless treatment for various
conditions. It is especially useful for sports injuries and other types of wounds, as it does not require
any downtime or anesthesia.
Platelet-rich plasma therapy is a new type of treatment in regenerative medicine that uses
components of the patient's own blood cells to boost the body's own healing process. The platelet
cells in platelet-rich plasma are the first response of the body to injury. PRP is packed with growth
factors that encourage the production of new, healthy tissue.To make platelet-rich plasma, the
patient's blood is spun in a centrifuge to separate red blood cells from platelets. This procedure is
then used to treat inflammation and promote healing.
This procedure is considered a safe procedure because it uses the patient's own blood. It also
doesn't cause an allergic reaction. As the body makes its own plasma, there is a low risk of side
effects. However, patients should keep in mind that the results are not permanent and additional
injections may be needed. PRP injections are effective in addressing problems such as male pattern
baldness and hair loss.
Artificial organs
The goal of artificial organs in regenerative medicine is to replace or augment organ function. Using
tissue engineering and 3-D printing, medical devices can be created to mimic the functioning of
human organs. Such organs can secrete hormones, nourish the vasculature, and grow with the
body. This technology could alleviate the shortage of organs and eliminate the need for organ
transplantation.
Currently, artificial organs are mainly used to replace a failing organ or limb. Organ transplants are a
lifesaving solution for severe injuries, but organs are very difficult to obtain and the recovery period is
long. During the transplantation process, patients may experience problems with circulation and may
need ventricular assistive devices.
Recently, organ manufacturers have developed 3D bioprinting to create organs. With this
technology, it is possible to print a human kidney or a thyroid gland. The process is still in its early
stages, but some impressive achievements have been achieved in this field. It has also been used to
create a human tibia replacement and a patch of beating heart cells. As this technology improves,
many more artificial organs may be made.
Although many advances have been made in this technology, only a few of them have reached
patients. Consequently, private clinics have sprung up to help fill the gap for patients. This
revolutionary technology could change the face of healthcare.
Gene transfection
Transfection is the process of introducing DNA or RNA into eukaryotic cells. It is a common method
in research to study gene regulation and protein expression. This technique also helps create
recombinant proteins. It is an important link between proteomics and genomics. In this webinar, we
will learn about the basic principles of transfection.
Transfection efficiency is determined by several factors. The nVGDS with a nuclear location
sequence enhances transfection efficiency by increasing the rate of nuclear uptake and
translocation. The nVGDS consists of a histone H1 based fusion peptide that contains the nuclear
localization signal of human immunodeficiency virus. This peptide promotes the translocation of
pDNA toward the nucleus.
Another important factor in cardiac transfection is the choice of appropriate ultrasound parameters. A
study in 2015 evaluated the efficiency of ultrasound-guided transfection of microRNA-21 in healthy
swine hearts. The authors found that ultrasounds with a 2 W/cm2 duty ratio and a 20-minute
duration were optimal for the successful transfection of microRNA-21.
Other approaches to gene transfection include polymer-based delivery systems. Polymers are
flexible and can be modified for different purposes. PEI is the most commonly used cationic polymer
vector. Its branched form is more efficient than its linear form. PEI/DNA complexes with a molecular
weight of 25 kDa were found to have the highest transfection efficiency.
Regulatory framework
The Regulatory framework for regenerative medicine (RM Act) governs the use of regenerative
medicine in medical institutions. The RM Act also sets standards and licensing schemes for
regenerative medicine facilities. In addition, the Act provides for the subcontracting of cell processing
tasks. The following are some of the key elements of the RM Act.
First, the regenerative medicine act protects the public from unapproved products and non-clinical
trials. It also covers the use of cells processed within or outside a medical institution for medical
treatments. The act does not apply to regenerative medicine products that have been marketed
under another name.
Secondly, a regenerative medicine product must meet certain safety and quality requirements.
These criteria are established by a national or regional medicines regulatory authority. In addition,
the regenerative medicine product should have the right to be sold in the market. This is a big
challenge because the established regulatory frameworks are based on small-molecule-based
medicines and do not adequately address the complexities of these new products. Thus, the
regulatory framework must be updated to accommodate the new class of medicines.
To make the regenerative medicine product marketable, a representative marketing company must
have the necessary licenses from the relevant governments. These companies must meet high
standards, including quality assurance, human resources, and post-marketing safety. These are the
key elements of the regenerative medicine regulatory framework.
The FDA recently issued guidance on the regulatory framework for regenerative medicine therapies.
At the same time, it announced its intention to exercise its enforcement discretion in some
regenerative medicine products. It also granted manufacturers at least three and a half years to find
the appropriate regulatory pathway and submit an application.
